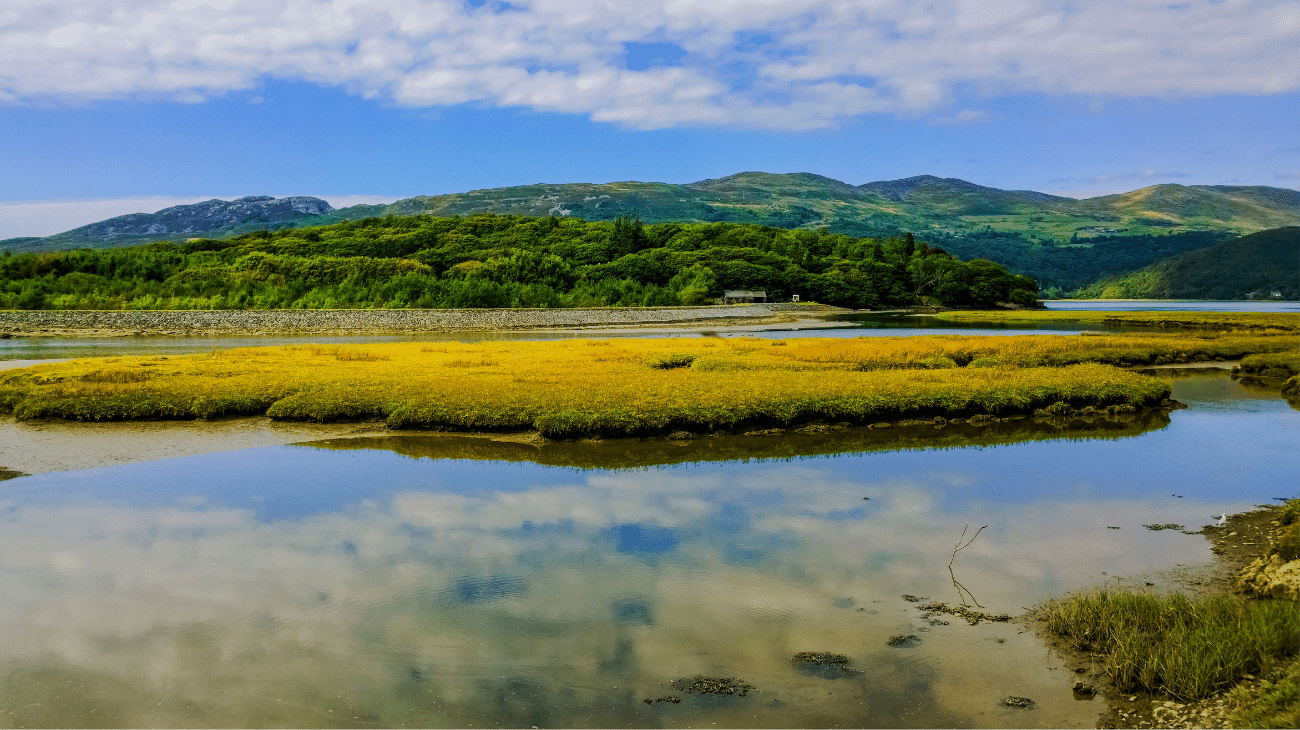
2 February marks World Wetlands Day, an important date to raise awareness of their future and the vital role these ecosystems play in biodiversity and human well-being, the theme of 2024.
What are the wetlands?
World Wetlands Day is celebrated on 2 February each year to commemorate the adoption of the International Convention on Wetlands of International Importance, better known as the Ramsar Convention signed on 2 February 1971 in the Iranian city of the same name.
Wetlands are transition areas between land and water, where water is the determining factor for the environment and the life of the species that live there; they are habitats for a wide variety of animal and plant species, many of which are rare or endangered.
These are environments characterised by the presence of water, which may be fresh, salt or brackish. They can be marshes, bogs, fens, lagoons, estuaries, mangroves and many other types of habitats. They perform a number of fundamental ecological functions, such as climate regulation, water purification, flood prevention and biodiversity conservation.
In addition, wetlands are important for our health and our well-being, as they provide food, drinking water and raw materials for industry.
However, we have lost more than 85% of these ecosystems to destruction and reclamation.
These areas are home to a wide variety of animals, including:
- Amphibians, some of the most common species include frogs, toads, salamanders and newts.
- Crustaceans, which feed on plants and aquatic animals, such as crayfish, crabs and even lobsters (in brackish areas).
- Insects can rely on food, water and places to breed in these areas; common species include dragonflies, butterflies, mosquitoes and flies.
- Mammals, including beavers, mink, badgers, foxes, deer and wild boar; these are adapted to life in or near water, and often feed on plants or aquatic animals.
- Fish, which feed on insects, larvae and other aquatic animals; these are trout, salmon, pike and eels.
- Birds, which find food, water and nesting places there, such as herons, ducks, geese, swans, flamingos and storks.
Wetlands and sustainability
Wetlands are important water reserves and help protect us from extreme weather events such as floods and droughts. In addition, they are crucial to our survival due to their role as carbon sinks and the fact that:
- counter climate change
- positively affect water purification
- protect against flooding
- return fibres and materials
- are home to thousands of related species.
Wetlands provide livelihoods and sustainable products for 62 million people who depend directly on fishing for a living, as well as timber for construction, vegetable oils, medicinal plants, fodder for animals, and stems and leaves for textiles.
To preserve wetlands, it is important to adopt some sustainable practices such as the careful and targeted management of water resources; this mass of soil and organic matter acts as a natural sponge, absorbing and retaining water during heavy rainfall and then gradually releasing it into the underlying soil and surrounding water bodies.
Research can help to better understand wetlands and the threats they face; it is important to raise awareness of the importance of wetlands and their benefits for the environment and biodiversity. Sustainable tourism can in fact be an opportunity to enhance wetlands and promote their conservation, through the creation of nature trails, the promotion of outdoor activities and the enhancement of local culture.
The future between threats and initiatives
Current threats to the future of wetlands are urbanisation, intensive agriculture, dam and weir construction, pollution and climate change. These factors can alter the ecological balance of wetlands and threaten the survival of the species that live there.
Protection at a global level requires a series of strategic and coordinated measures; it is important that all stakeholders work together to preserve wetlands and promote their conservation.
Local authorities can adopt policies and instruments for the protection of wetlands, such as the creation of protected areas and the promotion of sustainable agricultural practices.
Environmental organisations can raise awareness of the importance of wetlands and encourage sustainable practices.
Communities can actively participate in their management and promote sustainable tourism.
Also for 2024, on the occasion of this anniversary, numerous initiatives are planned all over the world, promoted by associations, public and private bodies. It is by loving wetlands and contributing to their protection that we can help ensure the future survival of these unique and fundamental ecosystems.
Play for the planet!